The AI framework “TensorFlow” is widely used to implement AI applications in the industrial field, but the AI framework “PyTorch” is highly popular in the research and academic fields, as it is easy to prototype. Therefore, there are many use cases such as porting and running AI models defined on PyTorch in x86-64 environments to embedded environments such as edge devices. Therefore, in this article, we will discuss the procedure for porting an AI model defined on PyTorch in an x86-64 environment to VIA AMOS-9100, a product based on NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX, an embedded environment, and VIA VAB-5000, a product based on MediaTek Genio 700. We will explain the inference speed of AI applications that can be built with this procedure. In addition, the evaluation in this article used “FCN-resnet50”, an AI model with a relatively large amount of computation. FCN-resnet50 is an AI model that provides segmentation capabilities to select pixels containing specific objects in an image. We hope this article has helped you understand the steps to port an AI model defined on PyTorch in an x86-64 environment to VIA’s edge AI products, and the effect of accelerators such as GPUs and APUs integrated into these hardware on inference speed.。
Click here for the product information of VAB-5000
Click here for product information of AMOS-9100
PyTorch and TensorFlow Market Share
The chart below presents a graph showing the adoption rate of each framework that shows which frameworks are used to implement machine learning-powered applications in the industrial sector (Source: State of Data Science and Machine Learning 2021). The most popular “Scikit-learn” library provides primitive functions related to machine learning, indicating that “TensorFlow” and its subset “Keras” are highly popular frameworks for deep learning, or AI. TensorFlow is chosen for its ease of deployment, not for its gentle learning curve to mastery. By adopting TensorFlow as a framework for developing AI applications, it is possible to optimize memory usage and computational graphs during deployment, so there are various cases of deploying large-scale AI models and cases of deploying AI models in environments with limited computing resources. Use cases. In addition, the adoption rate of PyTorch, a framework for AI, which is mentioned as a contrast to TensorFlow, ranks fifth in the industrial field.
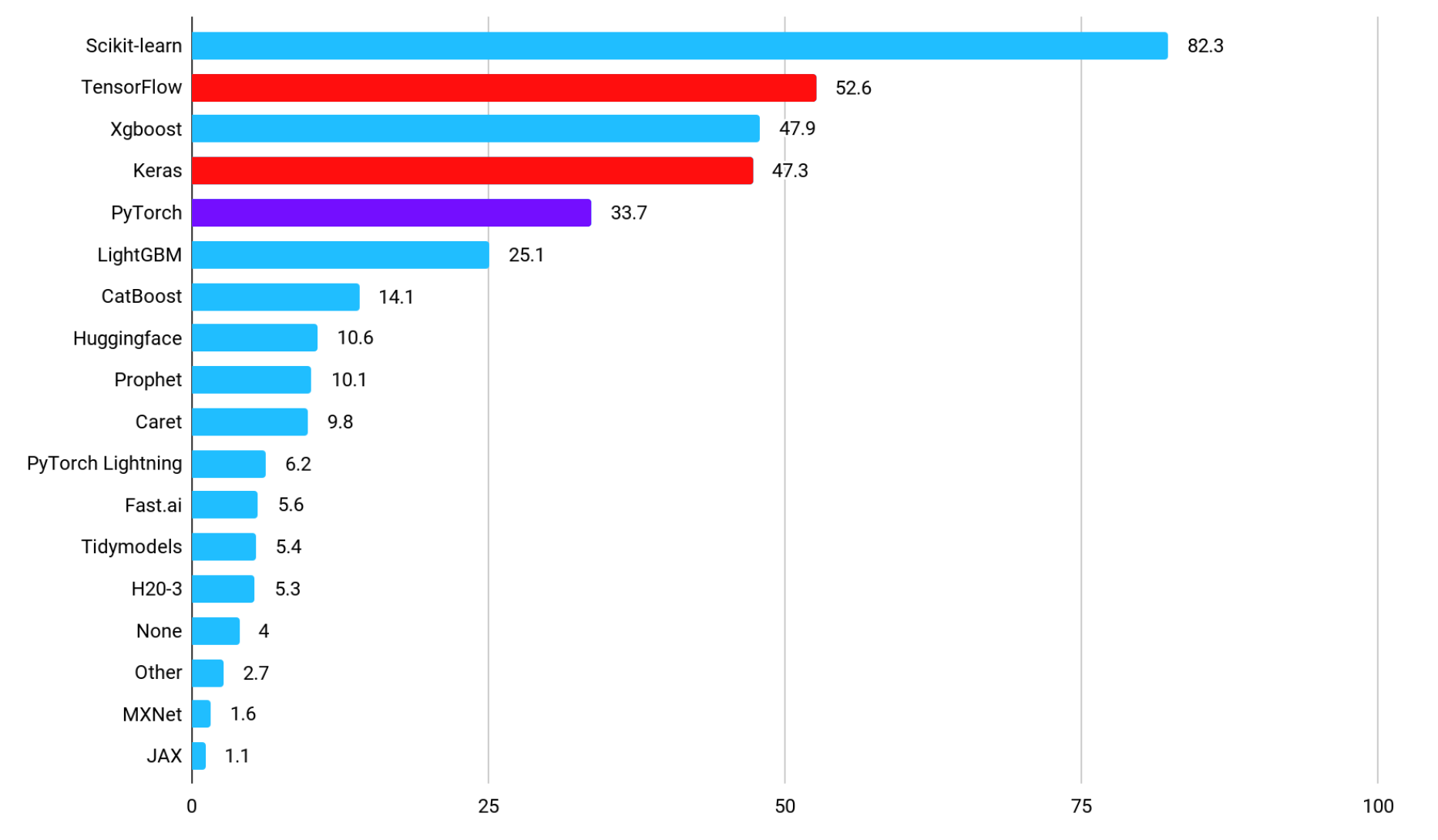
TensorFlow and PyTorch on Kaggle
PyTorch is highly popular in research and academic fields
On the other hand, the penetration rate of AI-oriented frameworks used for official implementation of papers in research and academia is shown in the figure below, and “PyTorch” is overwhelmingly popular (Source: ML Engineer comparison of Pytorch, TensorFlow, JAX, and Flax)。 The reason why PyTorch is widely used in research and academia is related to three features of PyTorch. The first feature is that PyTorch uses Python-like dynamic computational graphs, which are not only intuitive to code but also easy to debug. The second feature is that the use of dynamic computational graphs makes it easy to dynamically change the structure of the model, and it is relatively easy to implement conditional branching and loops, making it possible to quickly build complex models and implement new algorithms. One of its popular features is that PyTorch makes it easy to integrate with various open-source libraries, including Hugging Face and PyTorch Lightning. The third reason why PyTorch is chosen is that it makes it easier for AI model developers to collaborate with communities and ecosystems established for research purposes. PyTorch is widely adopted by communities that study deep learning, such as CVPR, NeurIPS, and ICML, and the latest research papers widely use PyTorch for their official implementation. PyTorch is also used in the official implementation of YOLOv12, an AI model that boosts high performance in object detection.

TensorFlow and PyTorch in Paper
AI models covered in this article
In this article, we will explain the inference speed of the AI model “FCN-resnet50” defined on PyTorch in the x86-64 environment when ported to the VIA AMOS-9100 or VIA VAB-5000.
AI Models for Segmentation – FCN-resnet50
FCN-resnet50 is an AI model that performs image segmentation, and outputs the likelihood of which object each pixel contains 21 types of objects for every pixel in the input image. FCN-resnet50 is a 50-layer fully convolutional network (Fully Convolutional Networks:FCN), and tends to have more computational intensity than general object detection AI models consisting of a convolutional layer and a fully coupled layer that outputs a bounding box. In this article, we will apply FCN-resnet50 to each frame of the video to identify the pixels that contain the dog object in the video. We will implement an AI application that masks and displays the pixels where the dog object exists as shown in the figure below on the x86-64 environment, on the AMOS-9100, and on the VAB-5000 to compare their performance.

Application Output
Evaluation method of inference performance in this article
The application implemented in this article feeds the AI model “FCN-resnet50” a square RGB format image of 288px x 288px cut from each frame of the video as input, and obtains a feature map with a likelihood of 288px x 288px showing which objects each pixel contains as output. Referring to the “likelihood that each pixel is the pixel that constitutes a dog” stored in a specific layer of the feature map, we create a mask for pixels with a likelihood of a certain value or more. The area containing the dog in real time is displayed as shown in the figure above. In this article, we evaluate the inference speed based on the FPS (Frames Per Second), which can be calculated from the time it takes to input a 288px x 288px RGB format image to the AI model and the feature map is output, and consider the optimal AI framework for the AMOS-9100 and VAB-5000. We also measured the time of the PostProcess to generate the masked output image from the feature map as a reference value. In this article, we will compare these performance measurements against applications implemented in 11 different environments with different hardware platforms, frameworks, and accelerator configurations, including the following: In addition, we used common OpenCV functions to implement the PreProcess process to cut out a square image from the video and the PostProcess process to generate a masked image from the feature map.
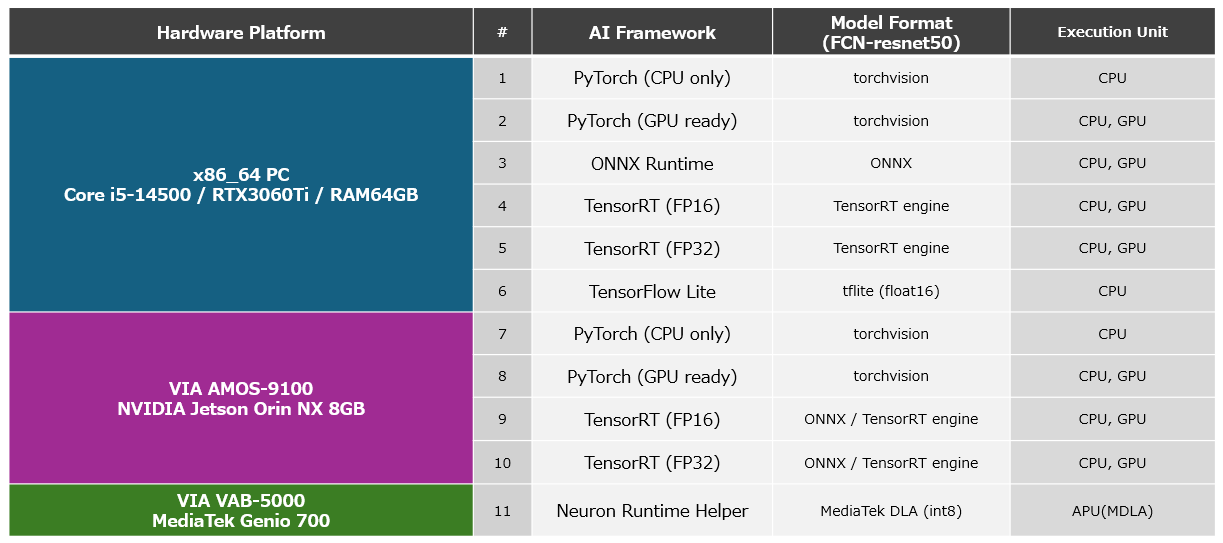
Platform List
Key frameworks used in machine learning and their features
In this section, we will discuss the main frameworks used to develop AI and their features before discussing the applications.
Features of PyTorch
PyTorch is an AI framework that encourages intuitive coding of AI models by providing a Python-like API. PyTorch uses a method called “Define-by-Run” to dynamically define computational graphs for defining AI models, allowing for flexible AI model modifications, complex AI model construction, and easy debugging of them. PyTorch is also suitable for prototyping and official implementation of AI models for research applications, allowing users to define custom layers, define original loss functions, and utilize AutoGrad capabilities, which are effective for training AI models with complex network structures. In addition, PyTorch also supports CUDA, a library for using GPUs as hardware accelerators, allowing for fast learning using GPUs. Although PyTorch has rarely been ported to embedded environments, it can be used to distribute models to various environments, including the edge, by exporting trained AI models in ONNX format, which will be described later.
ONNX Features
ONNX is a framework for enhancing interoperability that aims to enable the efficient exchange of trained AI models between different AI frameworks, such as PyTorch and TensorFlow. With ONNX, AI models running on various platforms, from the cloud to the edge, can be integrated into embedded applications with minimal effort. This makes it possible to deploy AI models implemented with PyTorch that boast a high performance in the cloud and the latest AI models that have just been developed and released for research purposes as AI models optimized for hardware resources at the edge using AI frameworks such as TensorFlow and TensorRT. Quickly develop advanced yet hardware-optimized AI applications. By using ONNX Runtime, ONNX AI models are not as optimized as PyTorch and TensorFlow, but they can also be embedded in applications in ONNX format and used for prototyping. This article also explains the inference speed of ONNX Runtime.
TensorFlow Features
TensorFlow is an ideal AI framework for deploying computationally intensive AI models or to the edge with limited hardware resources. Although the learning curve is a bit steeper compared to PyTorch, once mastered, you can optimize and deploy AI models for various platforms by leveraging TensorFlow Serving and TensorFlow Lite. PyTorch also offers deployment capabilities, but TensorFlow’s deployment capabilities have a better track record in production and are more widely used. Based on the MediaTek Genio 700, the VIA VAB-5000 can be used to generate DLA-formatted AI models optimized for APUs and GPUs using MediaTek’s toolset based on TensorFlow Lite AI models, enabling you to build high-speed AI applications that can efficiently utilize hardware accelerators. After implementing an advanced AI model with PyTorch to improve inference accuracy, it is converted into an AI model in TensorFlow Lite format via ONNX format. Development methods such as optimizing hardware resources, deploying to production, and building fast-running applications are the best solution for developing advanced systems.
Features of TensorRT (AMOS-9100)
TensorRT is an NVIDIA-specific framework for AI inference that can be used in NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX-based AMOS-9100 environments with NVIDIA GPUs, as well as x86-64 environments with NVIDIA GPUs. TensorRT focuses on the inference phase in AI, providing libraries optimized for inference and APIs to control it. TensorRT not only improves the inference speed of AI models, but also reduces memory consumption by actively utilizing variables in low-precision formats such as FP16 and INT8, as well as by integrating multiple layers of operations. Please note that AI models for TensorRT can be created from AI models in ONNX format. In this article, we will convert the AI model “FCN-resnet50” defined on PyTorch into an AI model for TensorRT via an AI model in ONNX format. The following describes the steps to be performed on the AMOS-9100 and its performance.
MediaTek NeuroPilot SDK/MDLA3.0 Features(VAB-5000)
MediaTek’s NeuroPilot SDK is an AI framework that can be used on products such as the VIA VAB-5000, which is based on SoCs equipped with APUs (MDLA3.0) such as the MediaTek Genio 700. By using the NeuroPilot SDK, you can convert TensorFlow-formatted AI models into DLA-formatted AI models optimized for Genio’s hardware, and use hardware accelerators such as GPUs and APUs integrated into Genio to achieve high-speed inference. In this article, we will convert the AI model “FCN-resnet50” defined by PyTorch into an AI model in DLA format via ONNX format and TensorFlow Lite format. We will introduce how to use VIA’s proprietary “Neuron Runtime Helper”, which is an execution framework, to run AI models on the VIA VAB-5000 at high speed and its performance.
MediaTek Genio 700 Product Overview (External Website)
MediaTek’s AI Solutions (External Website)
Optimize PyTorch Models for AMOS-9100
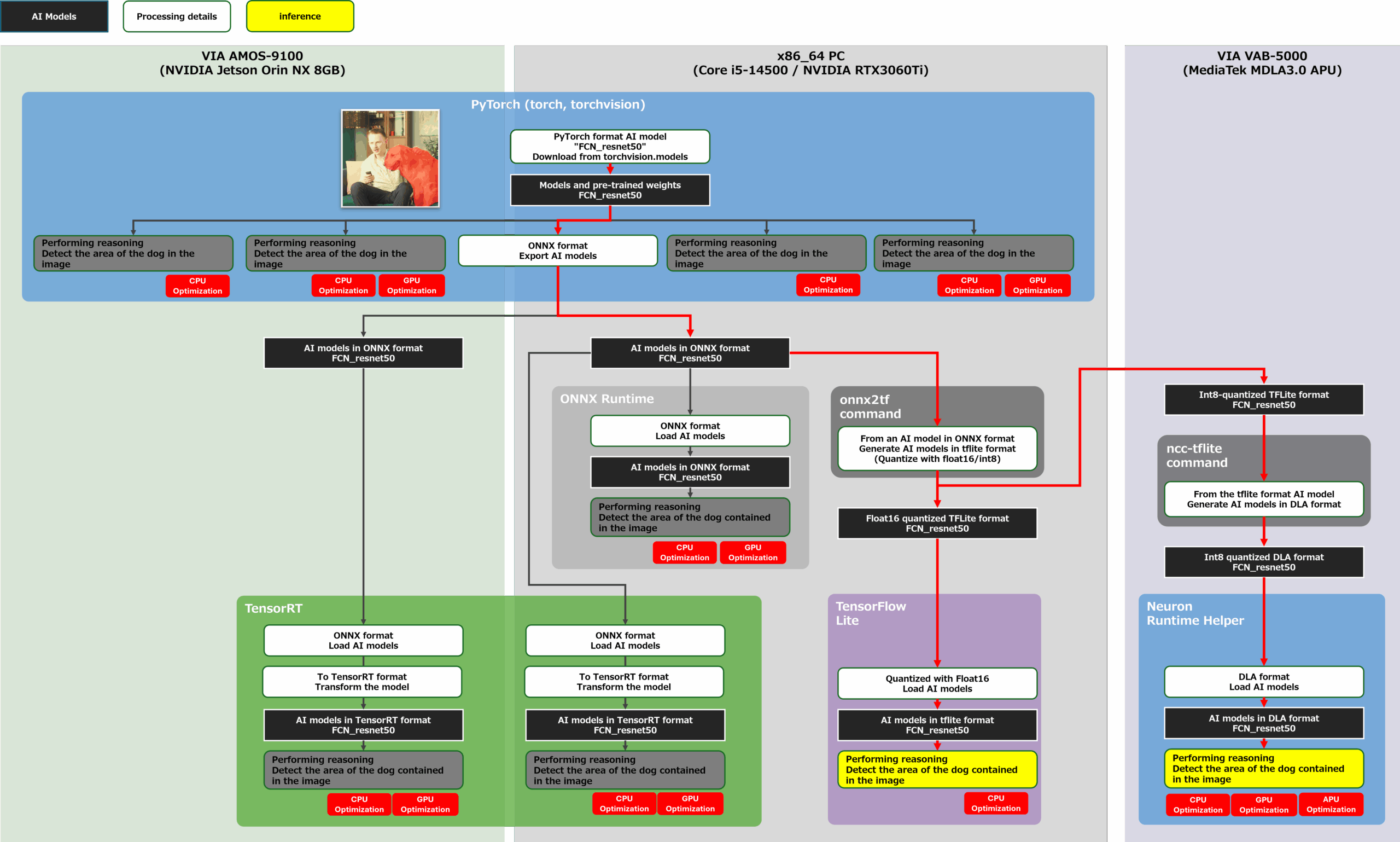
Let’s proceed with the development of porting the trained FCN-resnet50 defined on PyTorch to the AMOS-9100. The goal of this development is to measure the performance of the configuration shown in the yellow frame in the figure below. First, we measure the inference speed of FCN-resnet50 in each AI framework in the x86-64 environment, and then measure the inference speed of the AI model on PyTorch and the inference speed of the AI model on TensorRT, which specializes in GPU inference, in the AMOS-9100 environment. The AI model to be incorporated into the application to be measured was generated using the flow of the red line in the figure below.
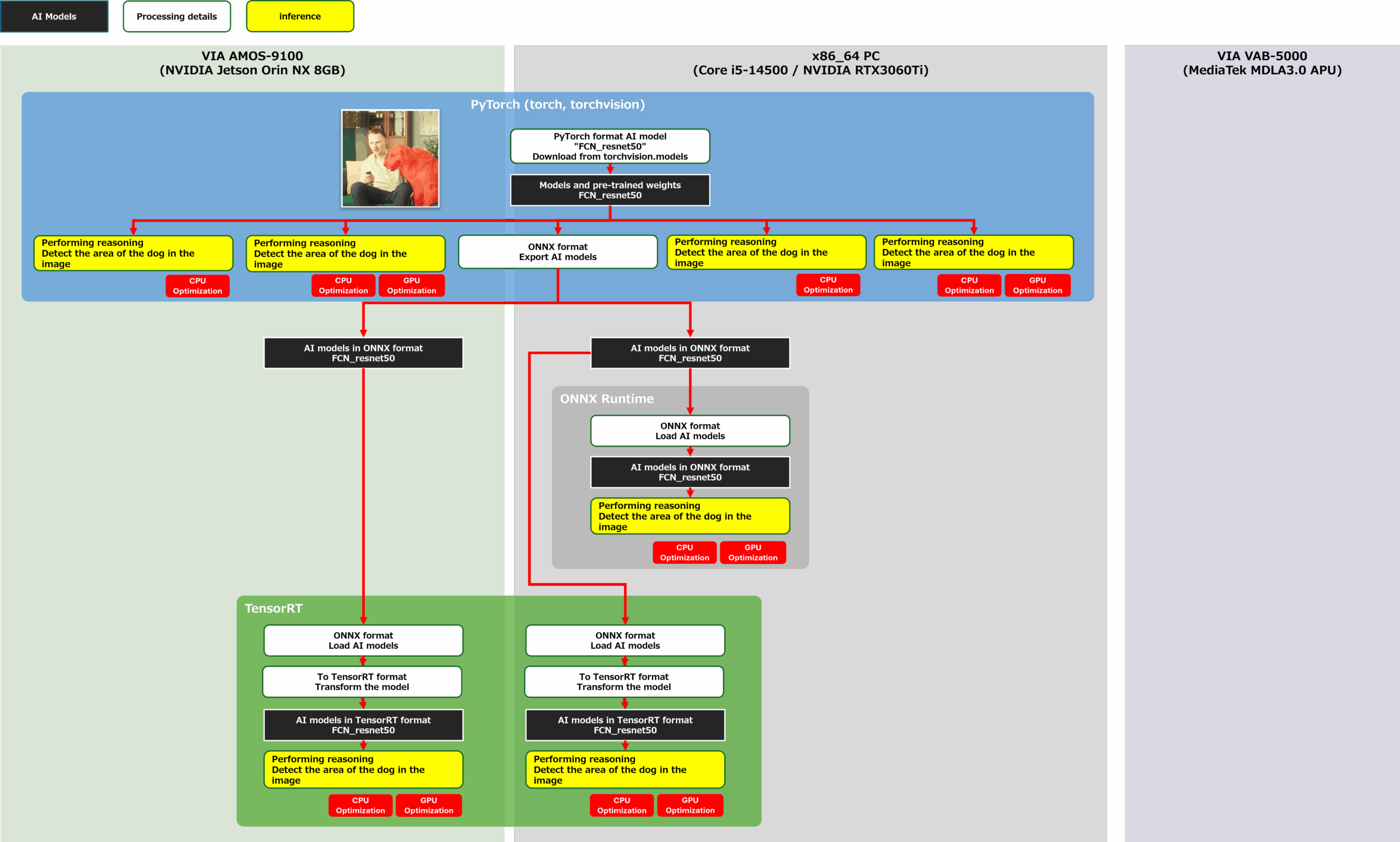
convert and eval PYTorch-TensorRT
You can find product information about AMOS-9100 here
To Define PyTorch Models in x86-64 and AMOS-9100 Environments
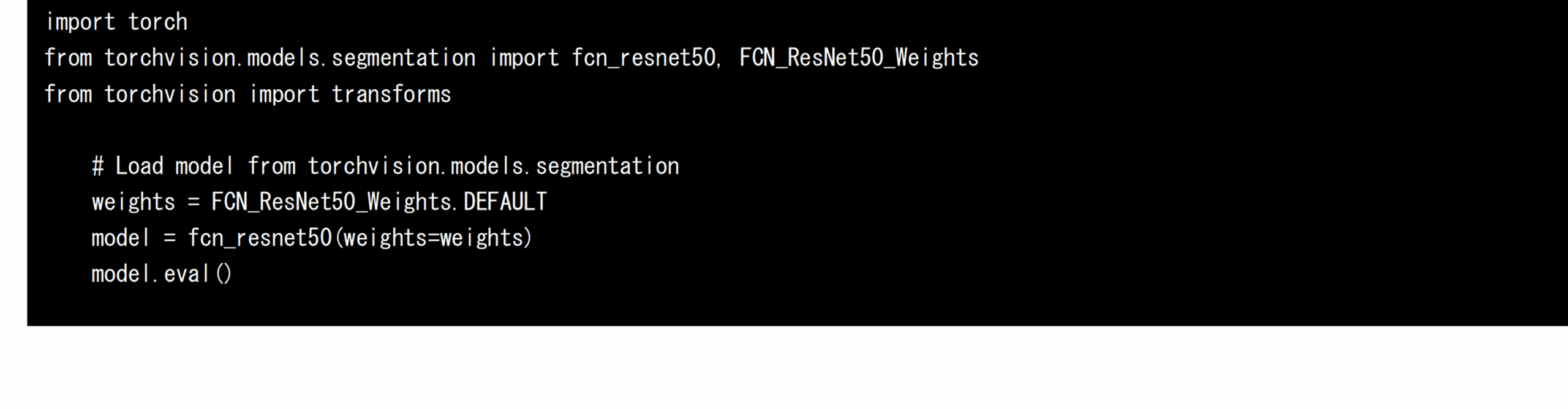
First, load the trained FCN-resnet50 using PyTorch’s torchvision package in x86-64 and AMOS-9100 environments. FCN-resnet50 with pre-trained weights is distributed on torchvision, an extension library of PyTorch, and you can get the AI model by simply running the following source code:
PyTorch uses the following source code to transfer the loaded AI model and the input tensor generated through PreProcess (see below) to the GPU, where it can be used to infer at high speed. If the transfer to the GPU is not performed, the CPU-only inference process will be performed. The CPU time before and after the inference was used to calculate the speed of each inference.

Tips for accurately measuring PyTorch performance.
Note that if you want to measure the inference time of an AI model using CPU time on PyTorch, you must call torch.cuda.synchronize() after invoking the inference process . This is because PyTorch’s inference processing with GPUs works asynchronously. By calling torch.cuda.synchronize(), you can guarantee that the inference process is complete, so you can accurately measure the time from the start of the inference to its completion. If you measure performance without calling torch.cuda.synchronize(), the CPU and GPU are synchronized for the first time when accessing the feature map from the CPU in the PostProcess process, so part of the inference time is in the processIt will be recorded in the processing time.
Define PostProcess and PreProcess in OpenCV
In this application, we used OpenCV to define the process of PreProcess to cut frames from the video and the PostProcess process to generate and display masked frames from the feature map obtained as a result of inference. The process flow of PreProcess and PostProcess is shown in the figure below.

convert tensor to from image
Convert AI models on PyTorch to ONNX format models
Next, export the trained FCN-resnet50 from PyTorch’s torchvision as an AI model in ONNX format. Since the size of the input tensor needs to be fixed when exporting, define a dummy input tensor and specify it as shown in the source code below. In this development, the shape of the input tensor of FCN-resnet50 was fixed to 288px x 288px and exported to the model.onnx file. Exported ONNX format AI models can be converted for other AI frameworks as well as leveraged ONNX Runtime for direct inference. In this development, the inference speed when using ONNX Runtime is also measured and evaluated.
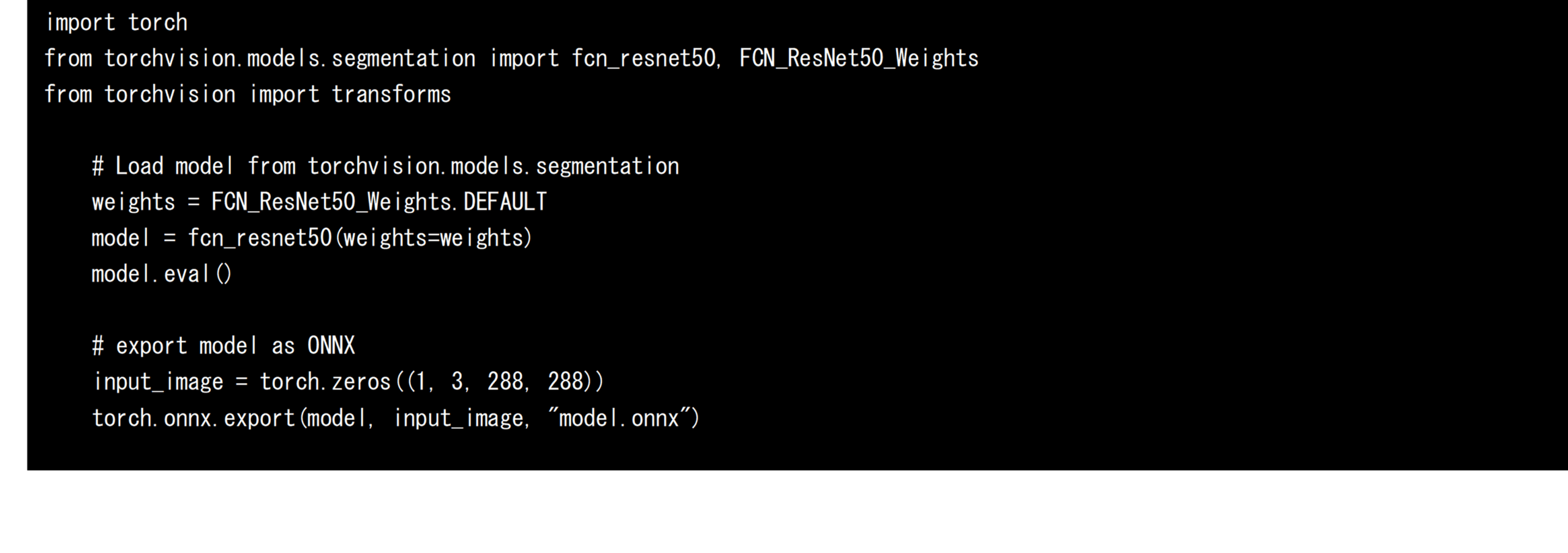
Convert ONNX format AI models to models for TensorRT
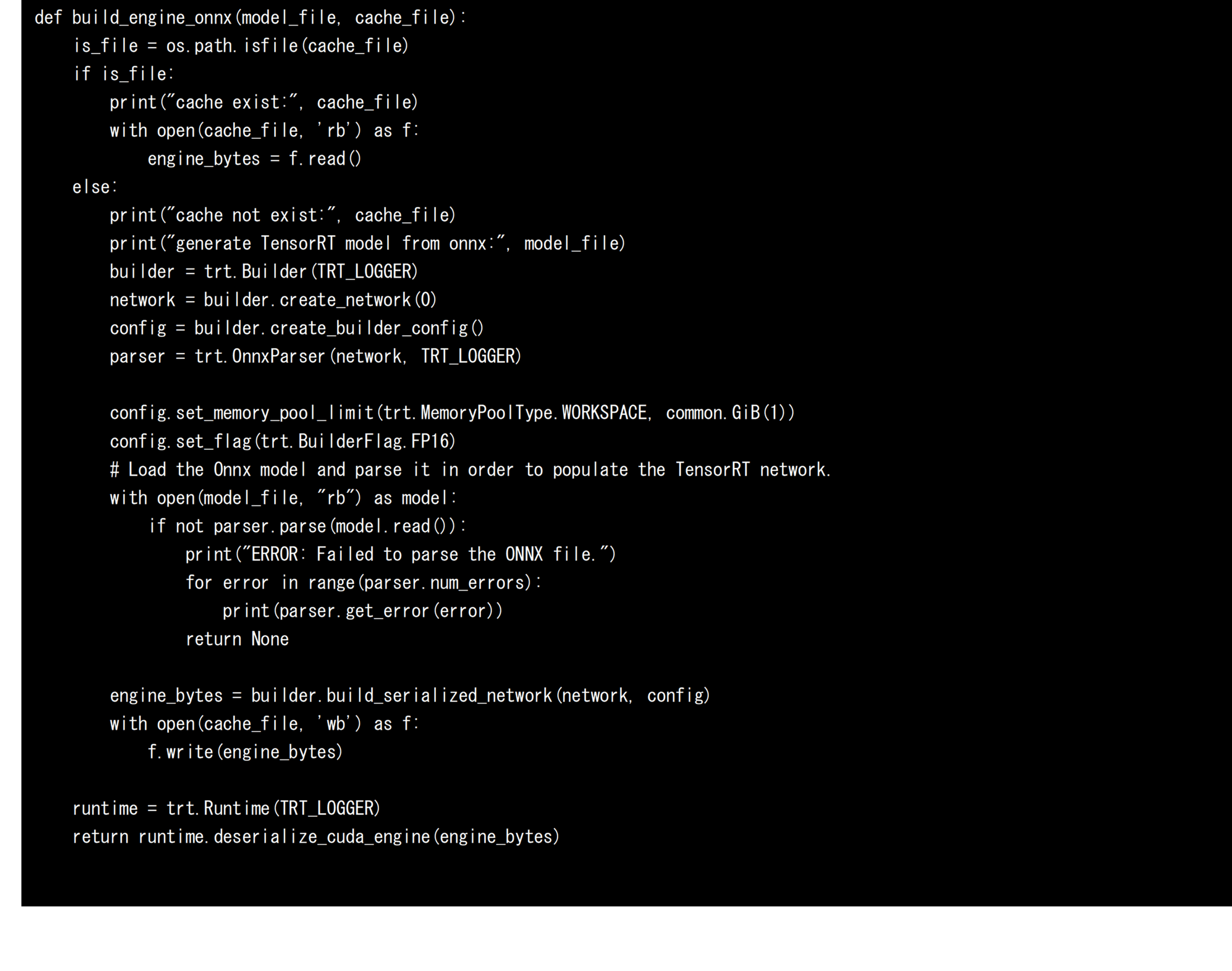
Next, we will convert the ONNX format AI model to an AI model for TensorRT to run AI models in AMOS-9100 and x86-64 environments with NVIDIA GPUs at high speed. When converting an AI model for TensorRT, four elements are defined and utilized: Builder, Network, Config, and Parser. Parser analyzes the AI model in ONNX format, and Network defines the computational graph. Config determines the options for conversion, and Builder generates an AI model for TensorRT. In this development, in order to optimize the AI model to FP16, we added “trt. BuilderFlag.FP16”. This designation allows for the generation of AI models for TensorRT optimized for FP16 that reduce memory usage and efficiently utilize compute units. If you do not specify this Config, the AI model will be optimized for FP32. Based on the above, the source code to convert an AI model in ONNX format into an AI model for TensorRT is shown below. Since model conversion requires a certain amount of time, in this development, the serialized AI model is saved in the engine file during the first conversion, and the saved AI model is loaded and used without calling the model conversion process during subsequent conversion. This is a speed-up technique that is also used in NVIDIA’s DeepStream framework.
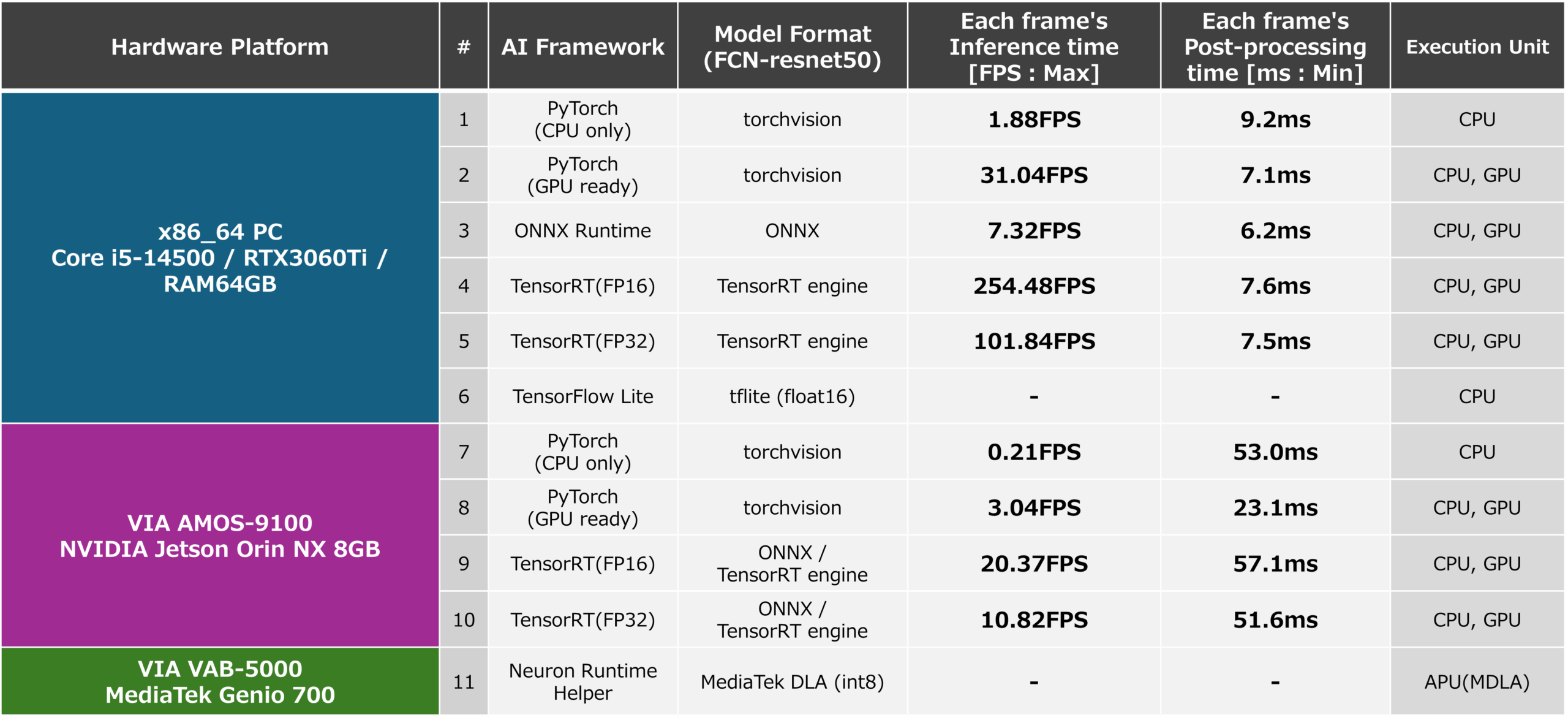
Comparison of PyTorch and TensorRT Performance in x86-64 and AMOS-9100 Environments
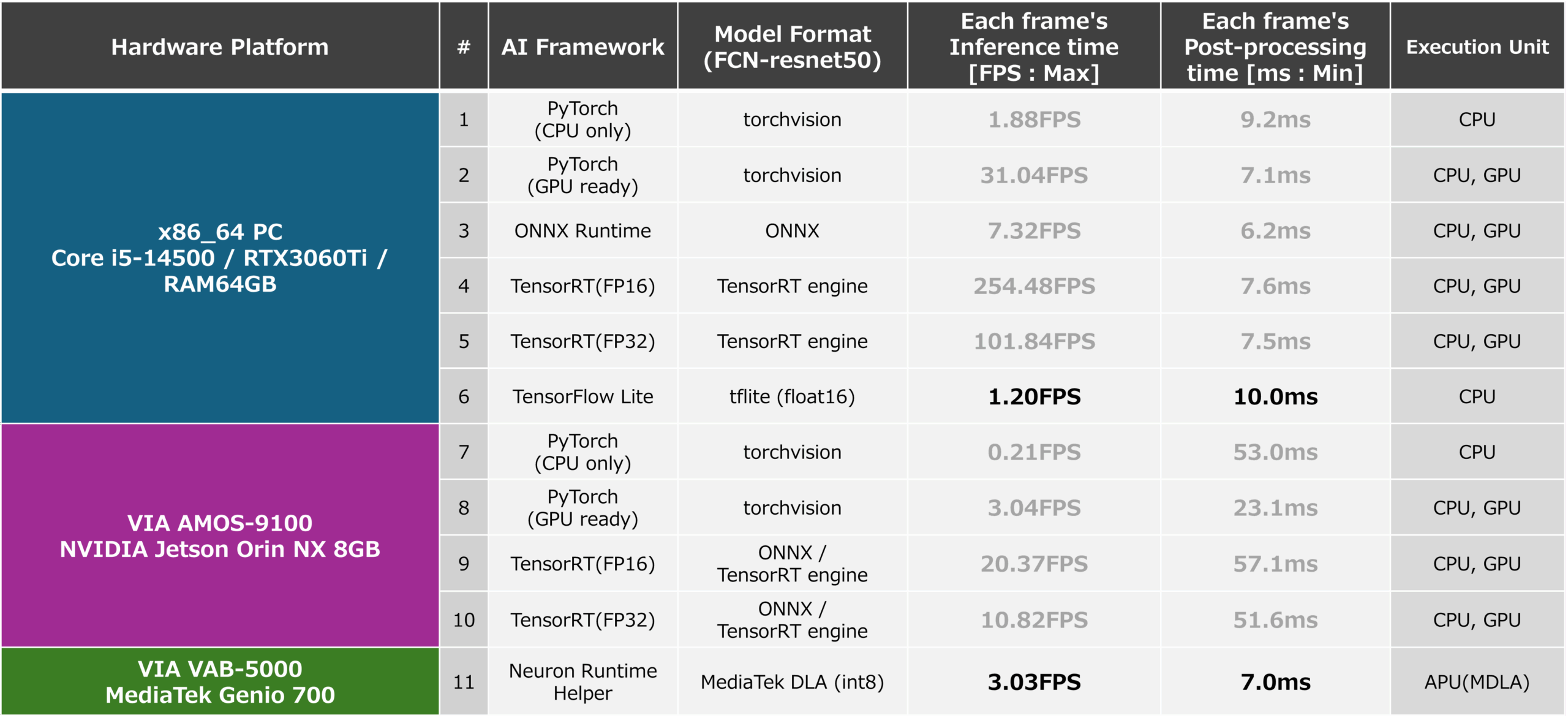
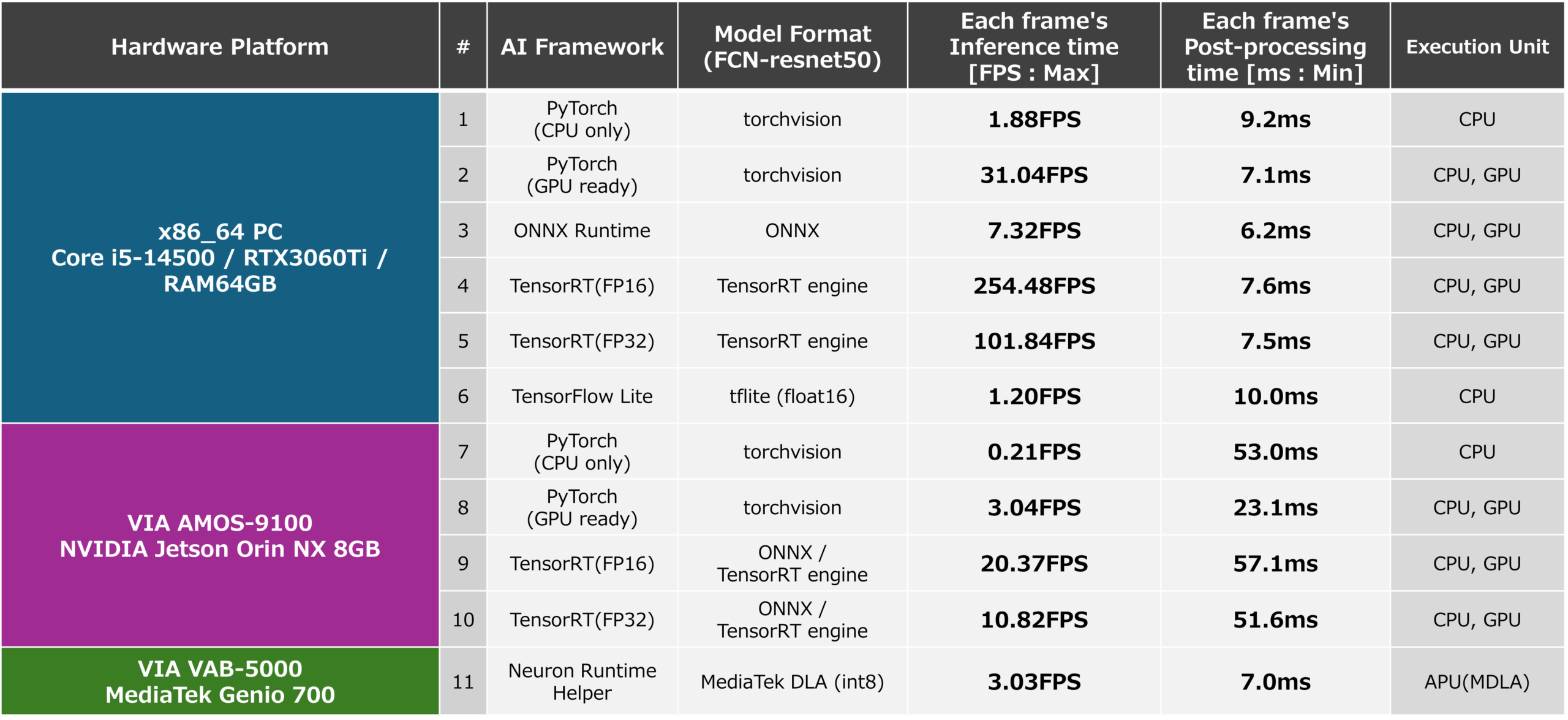
The inference speed (FPS) and PostProcess processing time for x86-64 and AMOS-9100 environments measured based on the above are shown below. In addition, the inference speed and PostProcess processing time when running an ONNX format AI model generated in an x86-64 environment using ONNX Runtime are also listed as reference values. From this result, it can be confirmed that inference using TensorRT, which can fully utilize the GPU, which is a computing resource, is very fast. Inference using ONNX Runtime and inference using PyTorch also run fast because they use GPUs, but they do not achieve optimization when using TensorRT, and the result is that inference speed is not sufficient. When generating a TensorRT AI model, you can use the “trt. BuilderFlag.FP16” and the inference speed is 5 and 10 as shown in the figure below. This is about half the inference speed of 4 and 9 in the figure below when configuring the model with FP16 type. From this, it can be seen that by using FP16, the CUDA cores and tensor cores installed inside the GPU can handle twice as many operations as FP32, and can benefit from FP16.
Based on the results of this study that the FCN-resnet50 AI model can be run at an inference speed of about 20 FPS by utilizing TensorRT on the AMOS-9100, it is possible to use the AMOS-9100 to control the robot andIt can be seen that it is possible to incorporate segmentation capabilities into applications where high real-time performance is essential, such as surveillance cameras.
PlatformList PyTorch TensorRT
Optimizing PyTorch’s Models for the VAB-5000
Next, let’s look at the inference speed of the trained AI model FCN-resnet50 defined on PyTorch and ported to the VIA VAB-5000 with the MediaTek Genio 700 at its core. The goal of this development is to measure the performance of the configuration shown in the yellow frame in the figure below. The AI model to be incorporated into the application to be measured was generated using the flow of the red line in the figure below. The evaluation using the TensorFlow Lite AI model was not to measure the inference speed, but to check whether the model was able to maintain its correctness.
convert and eval NeuronHelper
You can find product information about VAB-5000 here
Run DLA-formatted AI models faster with VIA’s Neuron Runtime Helper
In the Debian environment on the VAB-5000, the Python package “Neuron Runtime Helper” developed by VIA can be used to run AI models in DLA format at high speed with only a small amount of source code. To obtain an AI model in DLA format that can be run by Neuron Runtime Helper, first export FCN-resnet50 as an ONNX format AI model on an x86-64 environment, and then apply the onnx2tf command to the generated ONNX format AI model to convert the AI model to TensorFlow Lite format. Finally, the DC model in DLA format can be obtained by applying the ncc-tflite command to convert the AI model for Genio on the VAB-5000 to the AI model in TensorFlow Lite format (Figure above).
Converting ONNX models to DLA models via TensorFlow Lite format
In this development, in order to obtain an AI model in DLA format, the generated AI model in ONNX format will be converted into an AI model in TensorFlow Lite format, which will be an intermediate format. For this conversion, we used the onnx2tf command provided by the Python package. By executing the onnx2tf command with the argument “-oiqt”, you can generate multiple TensorFlow Lite AI models with various optimizations from an ONNX format AI model.
The following figure shows the AI models that can be generated by the onnx2tf command. The AI models that can be generated include[1] AI models that use INT8 for all operations (*_full_integer_quant),[2] AI models that use FP16 for all operations (*_float16),[3] AI models that use FP32 for all operations (*_float32), [4] An AI model that uses INT8 for basic operations and INT16 for the activation layer (16×8 quantization: *_full_integer_quant_with_int16_act),[5] FP16 is used for input and output, An AI model that uses INT8 for all other operations (*_integer_quant),[6] An AI model that uses FP16 for input and output, INT8 for basic operations, and INT16 for activation layers (*_integer_quant_with_int16_act),[7] There are a total of 7 types of AI models (*_dynamic_range_quant) that optimize the calculation graph without limiting the type. Of the seven AI models, except for *_full_integer_quant, six AI models contain instructions related to INT32 and FP32, which are not supported by the VAB-5000’s APU, making it difficult to port to the VIA VAB-5000.

ModelType by Quantization
In this development, in order to optimize the AI model for the APU of the VAB-5000, we select “model_full_integer_quant.tflite” from [1], which is a model that is fully optimized for INT8 among the generated AI models, and generate an AI model in DLA format optimized for INT8 using the following ncc-tflite command. I used it for inference on the VAB-5000.

Addressing the Decrease in Detection Accuracy Caused by AI Models Optimized for INT8
When an AI model in ONNX format is converted into an AI model in TensorFlow Lite format “model_full_integer_quant.tflite”, which defines all variables as INT8, and generates an AI model in DLA format, the variables inside the model change from FP32 to INT8, which reduces the accuracy of the values that can be held. Reduces object detection accuracy. This reduces the likelihood that the pixel contains a dog and increases the probability that the pixel contains a background. An issue occurs where the dog object is falsely detected as a background object and the object cannot be detected at all. In order to address this problem, in this development, for a feature map containing 21 types of objects, the Sofmat layer processing that adjusts the sum of the likelihoods of all objects to 1.0 (probability) is removed, and for output tensors with a total likelihood of 1.0 or more without using the Softmax layer, We have made it possible to detect pixels with a certain likelihood value or higher by treating them as dog objects.
Performance of DLA AI models running on the VAB-5000
The performance of an AI model in the FP16 optimized TensorFlow Lite format generated by the above steps when running on x86-64 with the TensorFlow Lite runtime and the performance of an AI model in DLA format optimized for INT8 is run by the Neuron Runtime Helper on the VAB-5000 are shown below. From the results, it was found that even the computationally intensive AI model “FCN_resnet50” can run at about 8 FPS by optimizing the model to INT8 and properly utilizing the VAB-5000’s CPU, GPU, and APU. This result makes the VAB-5000 suitable for applications in areas where latency tolerance is allowed, such as visual inspection equipment, access control, and video processing (generative AI), where low FPS is not a problem.
PlatformList NeuronHelper
Leverage AI models available from PyTorch to develop edge AI applications for the AMOS-9100 and VAB-5000
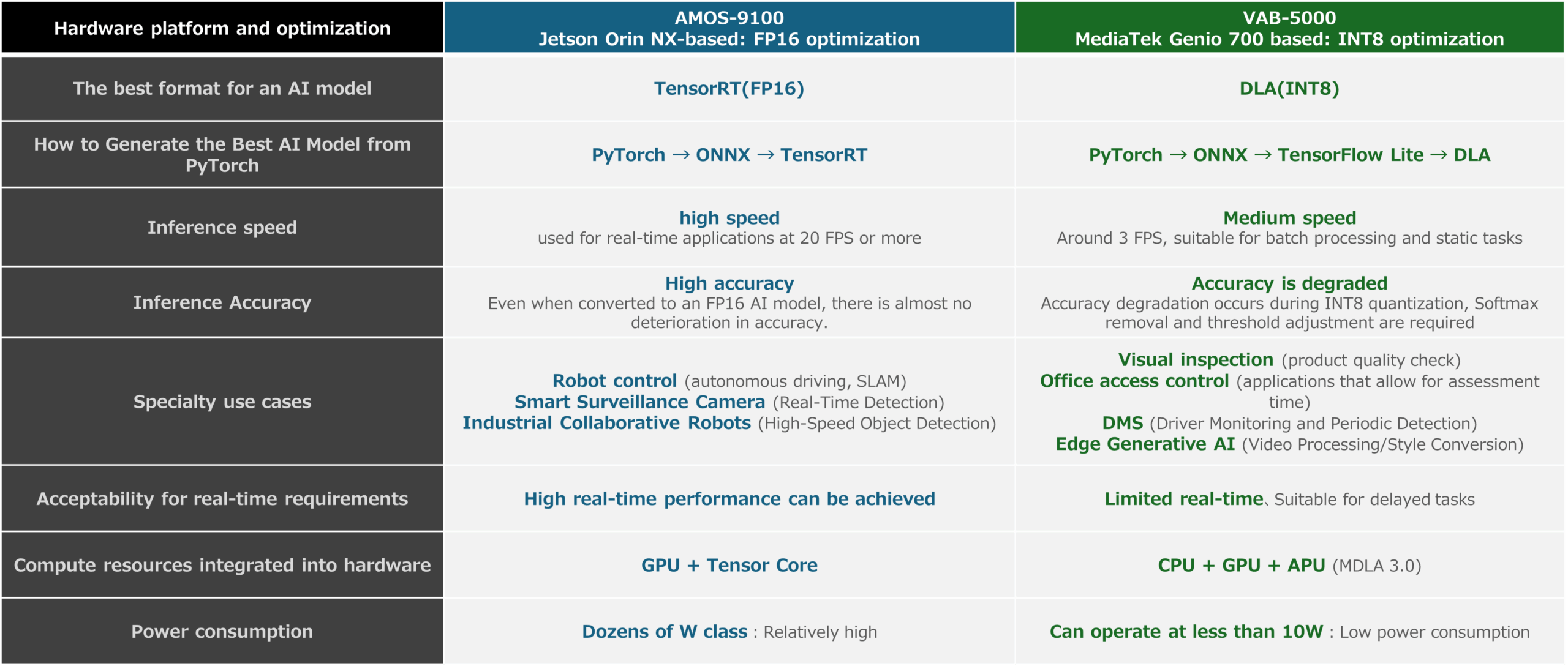
In this article, we introduced that relatively large computational AI models defined by PyTorch can be run on the AMOS-9100 and VAB-5000, and that they can run at a reasonable speed. The following figures show the features of the AMOS-9100 and VAB-5000 obtained through this article, as well as the recommended optimizations and use cases that each platform excels in, which can be derived from the measurement results. These results show that the AMOS-9100 is suitable for fields where real-time inference is required, while the VAB-5000 is suitable for fields where low power consumption is strongly required and latency can be tolerated.
In this article, videos that do not contain annotation data are treated as inputs for inference, so the evaluation of the inference accuracy of AI models is qualitative. In future articles, I would like to use input data with annotation data and label data to introduce quantitative results such as mAP and IoU.
PlatformList and Models
In addition, the inference speed that was measured by this development is summarized in the figure below. The results show that by leveraging AI models that apply their strengths, they can achieve reasonable inference speeds for their expected use cases.
PlatformList all

convert and eval ALL
AMOS-9100 and VAB-5000 with a wide range of AI models, including those distributed through the NVIDIA TAO Toolkit, NVIDIA GPU Cloud, and TensorFlow Hub
In previous articles, we have introduced the ability to use AI models provided by NVIDIA TAO Toolkit, NVIDIA GPU Cloud, TensorFlow Hub, and others for AI applications running on the VAB-5000. Based on the content of this article, it is possible to utilize AI models defined by PyTorch for the development of VAB-5000 and AMOS-9100, and can be used to build more advanced AI applications. Please use products such as the VAB-5000 and AMOS-9100 to develop edge AI products. VIA can also answer questions such as whether the VAB-5000 or AMOS-9100 is right for your application. Please feel free to contact us.
You can check the product information of VAB-5000 here.
You can find product information about AMOS-9100 here .
_a.png)